Betulins are natural products that occur in various plant species. They are lupane-type pentacyclic triterpenoids which exhibit a variety of intriguing biological effects. Vendors offer a variety of natural betulins, as well betulins carrying modifications that allow for site-specific functionalization, or increase the inherently low water solubility of betulin. Among those betulin derivatives are novel compounds not previously described in the literature.
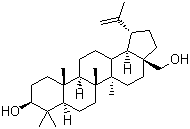
Betulin is a triterpene with a pentacyclic ring structure and hydroxyl groups in positions C3 and C28. Studies indicate that Betulin can effect intracellular signaling in ethanol-induced liver cells via inhibiting ROS, TNFα and TNFβ. In human cancer cells Betulin can induce mitochondrial cytochrome C release in human cancer cells, which results in apoptosis. Alternate studies on mice show that Betulin binds to melanocortin receptors and antagonizes the release of cAMP generation in mouse melanoma cells. Furthermore, Betulin has protective effects against cadmium induced apoptosis in human hepatoma cell lines. This occurs by inhibiting the activation of ROS, blocking Bid activation and suppressing the mitochondrial pathway.