|
Suppliers for CAS
3416-24-8
|
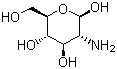
Properties | | CAS |
3416-24-8 | | Formula |
C6H13NO5 | | EINECS |
222-311-2 |
|
|
23 Registered suppliers
Dayang Chem (Hangzhou) Co.,Ltd.
P.R.China
Hangzhou Keying Chem Co., Ltd.
P.R.China
Xingrui Industry Co., Limited
P.R.China
Capot Chemical Co., Ltd.
P.R.China
More details are to be found here
Leap Chem Co., Ltd
P.R.China
Molecular Formula: C6H13NO5 Molecular Weight: 179.17
More details are to be found here
Tianjin Norland Biotech Co., Ltd.
P.R.China
Molecular Formula: C6H13NO5 Molecular Weight: 179.17
More details are to be found here
Hädener Rohstoffe GmbH
Switzerland
Molecular Formula: C6H13NO5 Molecular Weight: 179.17
More details are to be found here
New Natural Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.
P.R.China
Molecular Formula: C6H13NO5 Molecular Weight: 179.17
More details are to be found here
VMP Chemiekontor GmbH
Germany
Molecular Formula: C6H13NO5 Molecular Weight: 179.17
More details are to be found here
Unilong Industry Co.,Ltd
P.R.China
| Appearance | White powder
| | MW | 179.17
| | Purity | 99%
| | Boiling point | 311.69°C (rough estimate)
| | Density | 1.3767 (rough estimate)
| | Refractive index | 1.4240 (estimate)
| | Melting point | 88 °C |
Nantong Xindao Biotech Ltd
P.R.China
Lori Industry Co., Ltd
P.R.China
Hangzhou Lingrui Chemical Co., Ltd.
P.R.China
Skyrun Industrial Co., Ltd.
P.R.China
Carbone Scientific Co., Ltd.
U.K.
Xiamen Equation Chemical Co.,Ltd
P.R.China
Chemos GmbH & Co. KG
Germany
BuGuCh & Partners
Germany
Xenos Inc.
USA
Xi´an SR Bio-Engineering Co., Ltd.
P.R.China
Glucosamine is a common ingredient used in nutritional supplements to relieve joint pain.
Background
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a progressive and degenerative joint disease characterized by cartilage loss, bone changes, and synovial inflammation. Treatment with chondroprotective drugs (such as glucosamine sulfate) may have additional benefits over non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that treat the painful symptoms of OA. Glucosamine is commonly used over-the-counter to treat arthritis joint pain, although its acceptance as a drug treatment varies due to contradictions during clinical trials and findings of unclear clinical significance.
In theory, the administration of glucosamine provides a building block for the synthesis of glycosaminoglycans, slows the progression of osteoarthritis and relieves the symptoms of joint pain. So far, the research on the efficacy of glucosamine sulfate is inconclusive. Glycosaminoglycans contribute to the elasticity, strength and flexibility of articular cartilage. 11 A systematic review of various studies and guidelines determined that it was reported that patients taking glucosamine had moderate improvement in joint pain and function. A consistent narrowing of the joint space is observed, but the clinical significance is unclear.
Mechanism
The mechanism of action of glucosamine in joint health is unclear, however, there are several possible mechanisms that contribute to its therapeutic effect. Because glucosamine is the precursor of glycosaminoglycan, and glycosaminoglycan is the main component of articular cartilage, glucosamine supplements may help rebuild cartilage and treat the symptoms of arthritis. Some in vitro studies have shown that glucosamine can inhibit Interferon gamma reduces inflammation and nuclear factor kappa B subunit 65 (NF-κB p65), improving the symptoms of arthritis and joint pain.
Paul Schueller International Inc.
USA
Glucosamine is a common ingredient used in nutritional supplements to relieve joint pain.
Background
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a progressive and degenerative joint disease characterized by cartilage loss, bone changes, and synovial inflammation. Treatment with chondroprotective drugs (such as glucosamine sulfate) may have additional benefits over non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that treat the painful symptoms of OA. Glucosamine is commonly used over-the-counter to treat arthritis joint pain, although its acceptance as a drug treatment varies due to contradictions during clinical trials and findings of unclear clinical significance.
In theory, the administration of glucosamine provides a building block for the synthesis of glycosaminoglycans, slows the progression of osteoarthritis and relieves the symptoms of joint pain. So far, the research on the efficacy of glucosamine sulfate is inconclusive. Glycosaminoglycans contribute to the elasticity, strength and flexibility of articular cartilage. 11 A systematic review of various studies and guidelines determined that it was reported that patients taking glucosamine had moderate improvement in joint pain and function. A consistent narrowing of the joint space is observed, but the clinical significance is unclear.
Mechanism
The mechanism of action of glucosamine in joint health is unclear, however, there are several possible mechanisms that contribute to its therapeutic effect. Because glucosamine is the precursor of glycosaminoglycan, and glycosaminoglycan is the main component of articular cartilage, glucosamine supplements may help rebuild cartilage and treat the symptoms of arthritis. Some in vitro studies have shown that glucosamine can inhibit Interferon gamma reduces inflammation and nuclear factor kappa B subunit 65 (NF-κB p65), improving the symptoms of arthritis and joint pain.
Wilke International, Inc.
USA
Glucosamine is a common ingredient used in nutritional supplements to relieve joint pain.
Background
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a progressive and degenerative joint disease characterized by cartilage loss, bone changes, and synovial inflammation. Treatment with chondroprotective drugs (such as glucosamine sulfate) may have additional benefits over non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that treat the painful symptoms of OA. Glucosamine is commonly used over-the-counter to treat arthritis joint pain, although its acceptance as a drug treatment varies due to contradictions during clinical trials and findings of unclear clinical significance.
In theory, the administration of glucosamine provides a building block for the synthesis of glycosaminoglycans, slows the progression of osteoarthritis and relieves the symptoms of joint pain. So far, the research on the efficacy of glucosamine sulfate is inconclusive. Glycosaminoglycans contribute to the elasticity, strength and flexibility of articular cartilage. 11 A systematic review of various studies and guidelines determined that it was reported that patients taking glucosamine had moderate improvement in joint pain and function. A consistent narrowing of the joint space is observed, but the clinical significance is unclear.
Mechanism
The mechanism of action of glucosamine in joint health is unclear, however, there are several possible mechanisms that contribute to its therapeutic effect. Because glucosamine is the precursor of glycosaminoglycan, and glycosaminoglycan is the main component of articular cartilage, glucosamine supplements may help rebuild cartilage and treat the symptoms of arthritis. Some in vitro studies have shown that glucosamine can inhibit Interferon gamma reduces inflammation and nuclear factor kappa B subunit 65 (NF-κB p65), improving the symptoms of arthritis and joint pain.
Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.
USA
Glucosamine is a common ingredient used in nutritional supplements to relieve joint pain.
Background
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a progressive and degenerative joint disease characterized by cartilage loss, bone changes, and synovial inflammation. Treatment with chondroprotective drugs (such as glucosamine sulfate) may have additional benefits over non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that treat the painful symptoms of OA. Glucosamine is commonly used over-the-counter to treat arthritis joint pain, although its acceptance as a drug treatment varies due to contradictions during clinical trials and findings of unclear clinical significance.
In theory, the administration of glucosamine provides a building block for the synthesis of glycosaminoglycans, slows the progression of osteoarthritis and relieves the symptoms of joint pain. So far, the research on the efficacy of glucosamine sulfate is inconclusive. Glycosaminoglycans contribute to the elasticity, strength and flexibility of articular cartilage. 11 A systematic review of various studies and guidelines determined that it was reported that patients taking glucosamine had moderate improvement in joint pain and function. A consistent narrowing of the joint space is observed, but the clinical significance is unclear.
Mechanism
The mechanism of action of glucosamine in joint health is unclear, however, there are several possible mechanisms that contribute to its therapeutic effect. Because glucosamine is the precursor of glycosaminoglycan, and glycosaminoglycan is the main component of articular cartilage, glucosamine supplements may help rebuild cartilage and treat the symptoms of arthritis. Some in vitro studies have shown that glucosamine can inhibit Interferon gamma reduces inflammation and nuclear factor kappa B subunit 65 (NF-κB p65), improving the symptoms of arthritis and joint pain.
|


 details
details details
details details
details_Co_Ltd_1_575.jpg)








