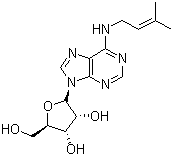
Description:
It is a cytokinin growth regulator that can be produced endogenously by plants to guide the differentiation of callus cells. In the research of anticancer drugs, it can induce cell cycle contraction and apoptosis.
- Molecular Weight: 335.36
- Molecular Formula: C15H21N5O4
Purity: ≥98%
Canonical SMILES:
CC(=CCNC1=C2C(=NC=N1)N(C=N2)C3C(C(C(O3)CO)O)O)C
InChI:
InChI=1S/C15H21N5O4/c1-8(2)3-4-16-13-10-14(18-6-17-13)20(7-19-10)15-12(23)11(22)9(5-21)24-15/h3,6-7,9,11-12,15,21-23H,4-5H2,1-2H3,(H,16,17,18)/t9-,11-,12-,15-/m1/s1
InChIKey: USVMJSALORZVDV-SDBHATRESA-N
- Boiling Point: 647.2±65.0°C at 760 mmHg
- Melting Point: >138°C (dec.)
- Solubility: Soluble in DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly, Heated, Sonicated)
- Appearance: White to Light Beige Solid
- Application: Plant Growth Regulators
- Storage: Store at 2-8°C
Synonyms:
N6-(2-Isopentenyl)adenosine; Isopentenyladenosine riboside; N-(3-Methyl-2-butenyl)-adenosine; 6-(3-Methyl-2-butenylamino)-9-β-D-ribofuranosylpurine; 6-(3-Methyl-2-butenylamino)purine riboside; 6-(γ,γ-Dimethylallylamino)purine riboside; N-Isopentenyladenosine; N6-(3-Methyl-2-butenyl)adenosine; NSC 105546; Riboprine; Isopentenyladenosine
More details are to be found on supplier website