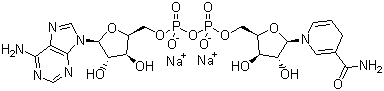Description:
NADH becomes oxidized to produce NAD+, NAD usually acts as a hydrogen acceptor, forming NADH which then serves as a hydrogen donor in the respiratory chain.Nutritional supplement in health care products.
- Molecular Weight: 709.41
- Molecular Formula: C21H27N7Na2O14P2
Purity: ≥92%
Canonical SMILES:
C1C=CN(C=C1C(=O)N)C2C(C(C(O2)COP(=O)([O-])OP(=O)([O-])OCC3C(C(C(O3)N4C=NC5=C4N=CN=C5N)O)O)O)O.[Na+].[Na+]
InChI:
1S/C21H29N7O14P2.2Na/c22-17-12-19(25-7-24-17)28(8-26-12)21-16(32)14(30)11(41-21)6-39-44(36,37)42-43(34,35)38-5-10-13(29)15(31)20(40-10)27-3-1-2-9(4-27)18(23)33;;/h1,3-4,7-8,10-11,13-16,20-21,29-32H,2,5-6H2,(H2,23,33)(H,34,35)(H,36,37)(H2,22,24,25);;/q;2*+
InChIKey: QRGNQKGQENGQSE-WUEGHLCSSA-L
- Melting Point: >188 °C
- Solubility: Soluble in DMSO
- Appearance: Off-White Solid
- Application: Ingredient of health care products.
- Storage: Store at -20 °C
Synonyms:
β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide disodium salt;disodium;[[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-oxidophosphoryl] [(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(3-carbamoyl-4H-pyridin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl phosphate;
More details are to be found on supplier website