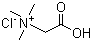Description:
Betaine, which is isolated from the roots of Beta vulgaris, has been shown to protect internal organs, improve vascular risk factors, and enhance performance. Databases of betaine content in food are being developed for correlation with population health studies. The growing body of evidence shows that betaine is an important nutrient for the prevention of chronic disease. Administration of Betaine inhibited inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, iNOS and COX-2.Nutritional supplement in health care products.
- Molecular Weight: 153.6
- Molecular Formula: C5H12ClNO2
Purity: >98%
Canonical SMILES:
C[N+](C)(C)CC(=O)O.[Cl-]
InChI:
1S/C5H11NO2.ClH/c1-6(2,3)4-5(7)8;/h4H2,1-3H3;1H
InChIKey: HOPSCVCBEOCPJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- Melting Point: 241-242 °C(lit.)
- Solubility: Soluble in DMSO
- Appearance: White cryst.
- Application: Ingredient of health care products.
- Storage: Store at -20 °C
Synonyms:
(carboxymethyl)trimethyl-ammoniuchloride; 1-carboxy-n,n,n-trimethyl-methanaminiuchloride; Achylin; Acidin; Acidine; Acidogeno; acidolhydrochloride; Acidol-Pepsin
More details are to be found on supplier website